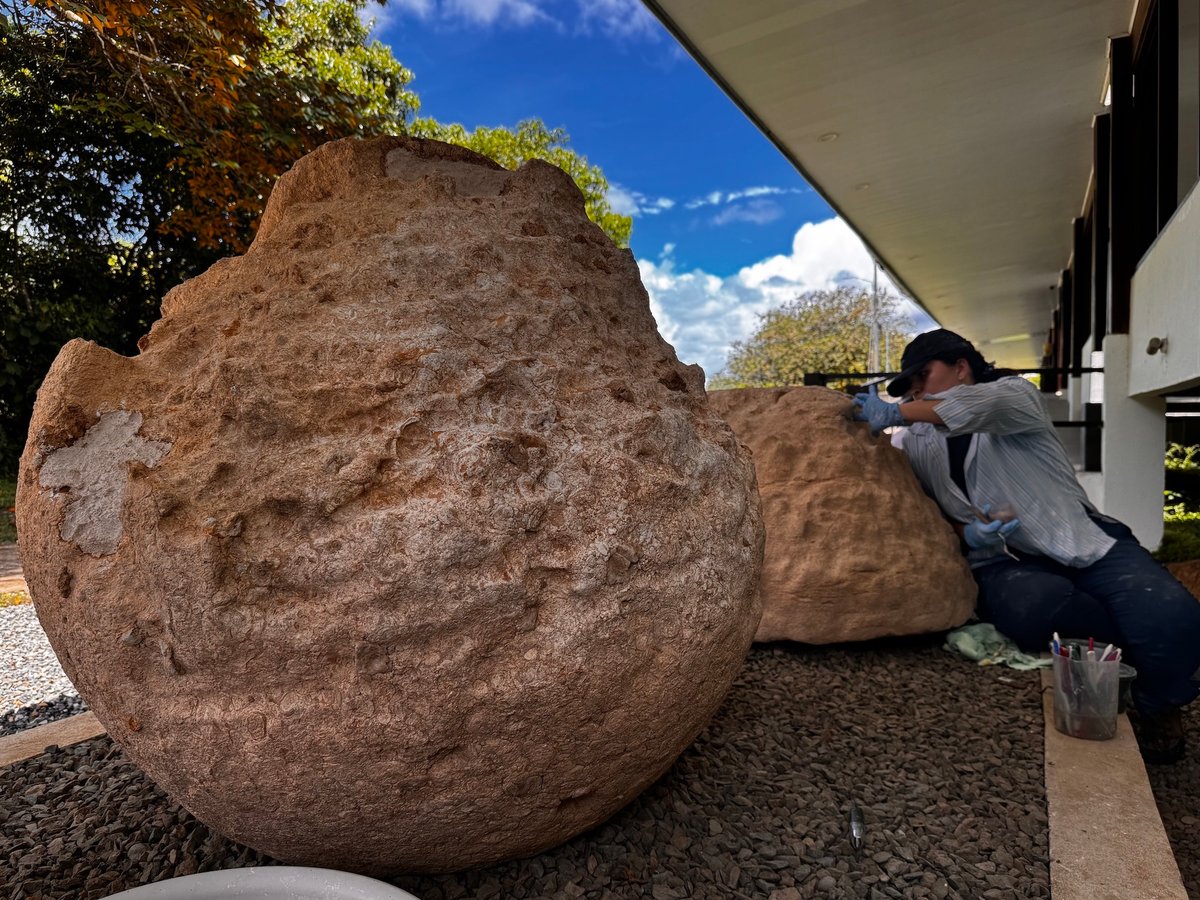
Specialists from Costa Rica and Mexico are restoring three pre-Columbian stone spheres, rare examples carved from limestone, at the Finca 6 Museum Site in Palmar de Osa in southern Costa Rica. The sculptures, attributed to the ancient Diquís culture, are part of the archaeological sites of the Diquís Delta, which were inscribed on the Unesco World Heritage list in 2014.
The Diquís culture flourished from around 500BC until Spanish conquest in the 16th century, producing one of the most distinctive sculptural traditions in the Americas. Crafted with stone hammers and polished with sand, the culture’s spheres are remarkable for their geometric precision.
The spheres undergoing restoration were found initially at the site known as Finca 4, one of a group of settlements built on the alluvial plains of the Sierpe and Térraba rivers. Finca 4 contains the largest known concentration of stone spheres, many of which are arranged in groups or geometric patterns linked to plazas and architectural structures. Archaeologists believe the spheres, ranging in size from a few centimetres to more than two metres in diameter, were placed to mark ceremonial spaces, processional routes or the dwellings of political leaders.
Unlike most of the more than 300 documented spheres, which were carved from hard igneous rocks such as gabbro and granodiorite, the Finca 4 examples now under treatment were sculpted from limestone conglomerate containing fossilised shells, snails and calcium deposits. Their unusual material has given them a pale, distinctive surface but also made them far more vulnerable to environmental damage.
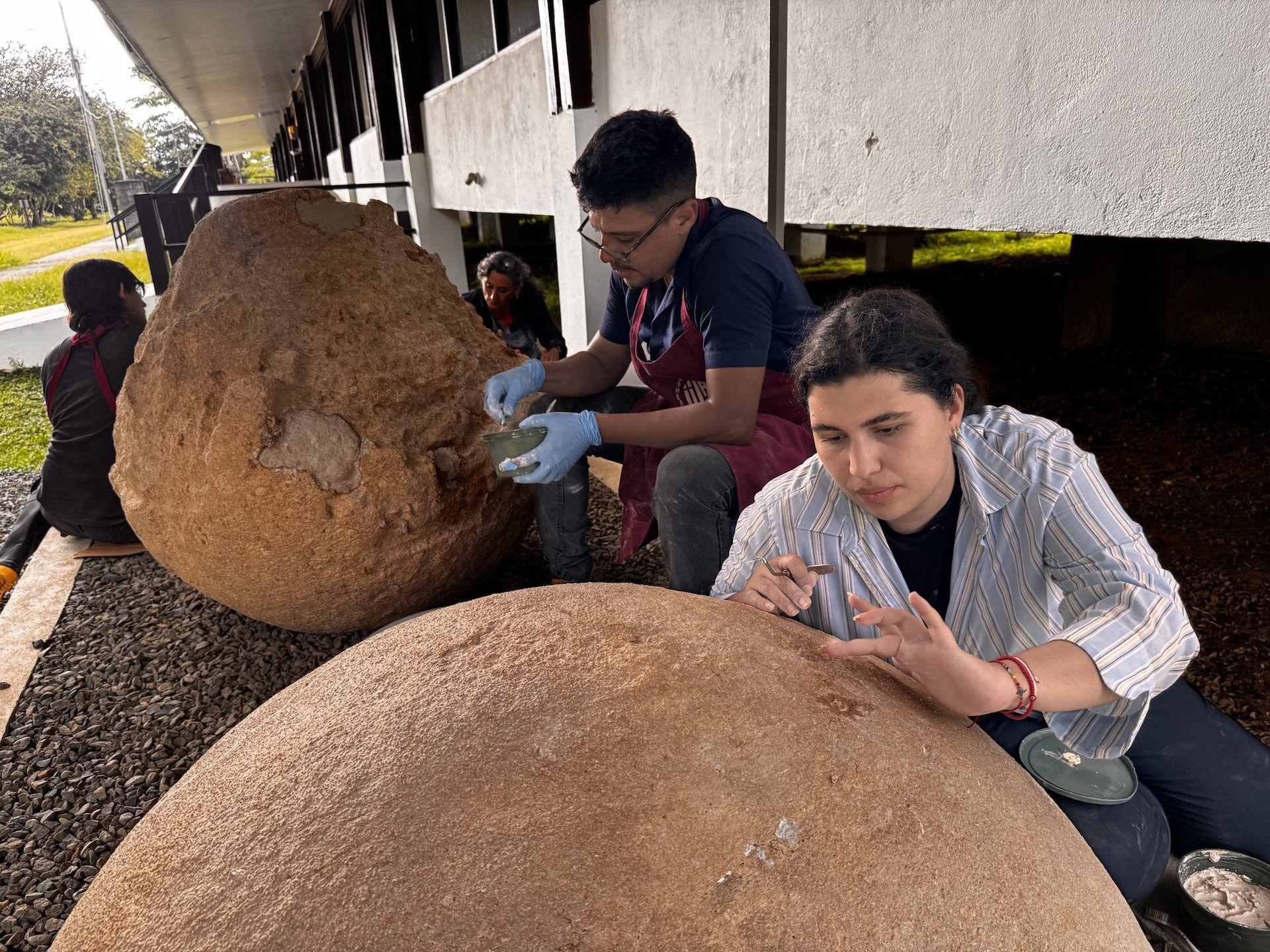
Restoration work underway on the ancient Diquís spheres at the Finca 6 Museum Site Courtesy Museo Nacional de Costa Rica
The conservation campaign, carried out in July and August, is part of a decade-long partnership between the Museo Nacional de Costa Rica and Mexico’s national school of conservation, restoration and museography, which is part of the Instituto Nacional de Antropología e Historia (INAH). At Finca 6, the team implemented a sequence of interventions, including mechanical cleaning under both dry and wet conditions, the removal of microorganisms using mild bactericides and chromatic reintegration using natural pigments. The reintegration is designed to distinguish between the spheres’ original and restored sections.
“In keeping with conservation principles, we are using materials that are compatible, reversible and retrievable, in other words, as close as possible to the original stone,” Mónica Pinillos, from Mexico’s school of conservation, restoration and museography, said in a statement. Beyond the direct conservation work, the project included the construction of new bases to stabilise the sculptures, a protective shelter to reduce exposure to sun and rain, and the installation of environmental monitoring systems to track temperature and humidity.
In addition to Mexico’s INAH, the project has garnered support from Costa Rica's Ministry of Culture and Youth and the country’s national museum, which have overseen the systematic conservation of the spheres for over a decade.